 路面分割-车道线条检测-深度估计模型python-onnx部署记录
路面分割-车道线条检测-深度估计模型python-onnx部署记录
杜老师课程学习记录,仅供个人学习使用,模型TensorRT部署之前的前处理和后处理分析,python简单实现。
# 路面分割模型
查看模型onnx文件,获得模型的输入输出维度:
输入维度:[1,3,512,896]
输出维度:[1,512,896,4]
模型是一个全卷积网络,输入和输出大小相同,不管模型多么复杂,先分析前处理和后处理,先用python实现。
预处理:标准化->cv2.resize()->维度切片->astype(np.float32)
源代码是直接使用的BGR格式,也不需要仿射变换。

# 车道线检测模型
输入维度:[1, 3, 288, 800]
输出维度:[1, 201, 18, 4]
用到的算法是Ultra-Fast-Lane-Detection,和熟悉的yolo系列检测算法还不太一样,Ultra-Fast-Lane-Detection是基于位置概率实现的。首先将连续的车道线离散成点,通过若干个点去表示车道线,因此问题转化为预测点的坐标,根据先验车道线肯定在路面上,而且在图片的下半部分,那么预先在图像高度方向上划分出若干条线,例如该模型是预先在高度方向上画18条线,即每条车道线会由18个点表示,并且18个点的y坐标已经确定好了,因此预测点(x, y)坐标转化成了只需要预测x坐标问题。
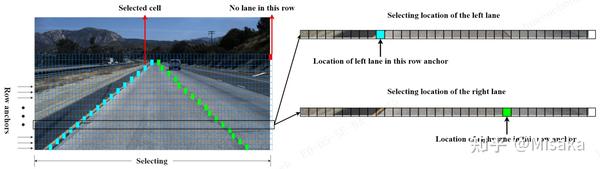
然后通过位置概率获得x坐标值,大概可以理解为:按图像的宽度方向,把图像分为若干个位置,比如该模型是把图像宽度分成了200个位置,再加上一个点不在图像上位置,那么总共就是201个位置,每个位置模型会输出一个位置概率,即表示点落在该区域的概率,因此模型输出维度[1, 201, 18, 4],可以理解为:201个位置概率(宽度方向格子数),一条车道线由18个点表示(y轴方向上的划线数),4表示业务场景只存在4条车道线。
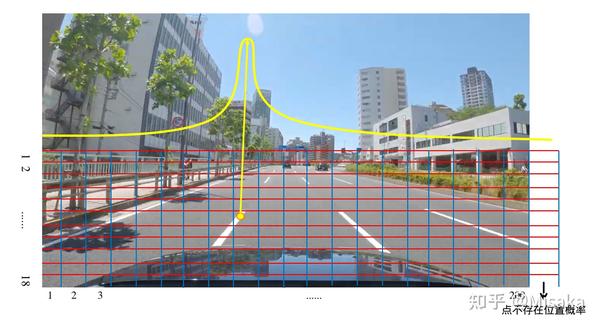
那么如何通过模型结果得到x坐标:首先对模型输出结果在201这个维度上计算softmax(),获得位置概率 O_{probability},然后位置编号点乘位置概率 O_{probability}后相加得到 O_{mul} ,再判断位置概率O_{probability}最大的位置是否是200(对应图像上的201,即点不存在的情况),如果是,表示点不存在,将O_{mul}中对应索引元素置为0,即过滤该点。
预处理步骤:
cv2.resize(image, (288, 800)),这里注意的是直接resize,刚开始以为是裁剪图像,只保留图像的下半部分,发现输出结果不对。
BGR->RGB
标准化并转化为np.float32
维度切片:(1, height, width, 3)->(1, 3, height, width)
后处理步骤:
模型输出的维度其实是:(1, 1, 201, 18, 4)
对201维度进行softmax(),得到位置概率O_{probability}
位置概率和位置编号点乘,之后求和得到O_{mul},O_{mul}维度为(18, 4)
判断位置概率O_{probability}最大的位置是否是200,如果是,将O_{mul}中对应索引元素置为0。
后处理可以直接写进onnx,可以省略C++代码编写量。

# 深度估计
输入维度:[1,3,256,512]
输出有六个,估计是全卷积网络反卷积过程的每个阶段都输出了,使用时取最后一个就好了,维度为[1, 1,256,512]
预处理:cv2.resize()->(BGR->RGB)->标准化->维度切片和np.float32
后处理:源代码中有个裁剪操作,把图像上面的18%裁剪掉了,并且对输出结果out*(-5)+255,便于可视化。

import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
'''
预处理和后处理步骤:
1:路面分割
预处理:
标准化:normalize=(image-mean)*norm
输入图像尺寸:不需要仿射变换,直接resize,512*896
输入图像格式:BGR
np.float32
输出图像通道:4通道
2:车道线检测
预处理:
cv.resize
标准化
BGR->RGB
np.float32
输出维度:1*1*201*18*4,201表示位置,18表示车道线由18个点表示,4表示有4根车道线
后处理:
201维度:softmax
点乘相加
200位置点 out_j置0
3:深度估计
输入[1,3,256,512]
输出有6个,估计是全卷积网络反卷积过程的每个阶段都输出了
使用时取最后一个就好
前处理:
resize()
BGR->RGB
标准化
切片和np.float32
后处理:
裁剪
out *(-5)+ 255
'''
#路面分割
def loadSegment(onnxFile, imgFile, size):
width, height = size
oriImg = cv2.imread(imgFile)
image = cv2.resize(oriImg, size).astype(np.float32)
#ascontiguousarray()内存不连续的数组,变为连续的数组,加快运行速度
imgTensor = np.ascontiguousarray(image.transpose(2,0,1).reshape(-1,3,height, width))
sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(
onnxFile,
providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
output = sess.run(None, {input_name: imgTensor})
out = output[0][0].transpose(2,0,1)
cv2.imwrite("segment.jpg", out[0]*255)
#车道线检测
def UltraFastLaneDetection(onnxFile, imgFile, size):
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
width, height = size
oriImg = cv2.imread(imgFile)
# image = oriImg[-288:, :, :]
image = cv2.resize(oriImg, size)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image = image/255.0
image = (image - mean)/std
image = image.astype(np.float32)
imgTensor = image.reshape(-1, height, width, 3).transpose(0,3,1,2)
print(imgTensor.shape)
sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(
onnxFile,
providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
output = sess.run(None, {input_name: imgTensor})
print(np.array(output).shape)
# 打印结果
out = np.array(output[0])[0]
griding_num = 200
col_sample = np.linspace(0, 800 - 1, griding_num)
col_sample_w = col_sample[1] - col_sample[0]
out_j = out
out_j = out_j[:, ::-1, :]
prob = scipy.special.softmax(out_j[:-1, :, :], axis=0)
idx = np.arange(griding_num) + 1
idx = idx.reshape(-1, 1, 1)
loc = np.sum(prob * idx, axis=0)
out_j = np.argmax(out_j, axis=0)
print(out_j)
loc[out_j == griding_num] = 0
out_j = loc
row_anchor = [121, 131, 141, 150, 160, 170, 180, 189, 199, 209, 219, 228, 238, 248, 258, 267, 277, 287]
cls_num_per_lane = 18
img_w, img_h = oriImg.shape[1], oriImg.shape[0]
for i in range(out_j.shape[1]):
if np.sum(out_j[:, i] != 0) > 2:
for k in range(out_j.shape[0]):
if out_j[k, i] > 0:
ppp = (int(out_j[k, i] * col_sample_w * img_w / 800) - 1,
int(img_h * (row_anchor[cls_num_per_lane - 1 - k] / 288)) - 1)
cv2.circle(oriImg, ppp, 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv2.imwrite("ultra-lane-draw.jpg", oriImg)
#深度估计
def ldrn(onnxFile, imgFile, size):
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
width, height = size
oriImage = cv2.imread(imgFile)
image = cv2.resize(oriImage, size)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image = image/255.0
image = (image - mean) / std
image = image.astype(np.float32)
imgTensor = image.transpose(2,0,1).reshape(1, 3, height, width)
sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(
onnxFile,
providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
input__name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
output = sess.run(None, {input__name: imgTensor})
print(np.array(output[5]).shape)
out = np.array(output[5]).reshape((256, 512))
# 源代码中有个裁剪和*(-5) - 255的操作,给它加上
out = out[int(out.shape[0] * 0.18):, :]
out = out * -5 + 255
plt.imshow(out)
plt.show()
# cv2.imwrite("ldrn.jpg", out)
if __name__ == "__main__":
segFile = "road-segmentation-adas.onnx"
# ultraFile = "ultra_fast_lane_detection_culane_288x800.onnx"
# ldrnFile = "ldrn_kitti_resnext101_pretrained_data_grad_256x512.onnx"
imgFile = "dashcam_00.jpg"
loadSegment(segFile, imgFile, (896,512))
# UltraFastLaneDetection(ultraFile, imgFile, (800, 288))
# ldrn(ldrnFile, imgFile, (512, 256))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
